Simple Meal Prep Ideas for a Busy Week


Understanding Heart Disease and Cardiovascular Health
Okay, let's talk about heart disease. It's a big one, right? Actually, it *is* the leading cause of death for both men and women in many parts of the world. Heart disease, or cardiovascular disease (CVD), is a broad term that encompasses a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. These conditions include coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, arrhythmias, and congenital heart defects. Understanding the basics is the first step towards taking control of your heart health.
Key Risk Factors for Heart Disease: Identifying Cardiovascular Vulnerabilities
Several factors can increase your risk of developing heart disease. Some of these, like family history, you can't change. But thankfully, many others *are* within your control. Let's break down the most important risk factors.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Managing Your Cardiovascular Pressure
High blood pressure puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels, making them weaker over time. It's often called the "silent killer" because many people don't even know they have it. Regular monitoring is key. Aim for a blood pressure reading below 120/80 mmHg. Lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can make a big difference. Medications are also available if lifestyle changes aren't enough.
High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia): Maintaining Healthy Cholesterol Levels for Heart Health
Cholesterol is a waxy substance that can build up in your arteries, forming plaques that narrow the passageways and restrict blood flow. There are different types of cholesterol. You want to keep your LDL ("bad") cholesterol low and your HDL ("good") cholesterol high. Again, diet plays a crucial role. Limit saturated and trans fats, and eat plenty of fiber. Exercise also helps boost HDL cholesterol. Statins are a common type of medication used to lower LDL cholesterol.
Smoking: Eliminating Tobacco Use for Optimal Cardiovascular Function
Smoking is terrible for your heart. Period. It damages blood vessels, increases blood pressure, and raises your risk of blood clots. Quitting smoking is the single best thing you can do for your heart health, and your overall health, for that matter. There are many resources available to help you quit, including nicotine replacement therapy, medications, and support groups. Don't give up, and seek help if you need it.
Diabetes: Controlling Blood Sugar Levels to Protect Your Cardiovascular System
Diabetes increases your risk of heart disease because high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels. If you have diabetes, it's essential to manage your blood sugar levels effectively through diet, exercise, and medication. Work closely with your doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Obesity and Overweight: Achieving and Maintaining a Healthy Weight for Cardiovascular Well-being
Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your heart and increases your risk of other heart disease risk factors, like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. Losing even a small amount of weight can have a significant impact on your heart health. Focus on a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and portion control.
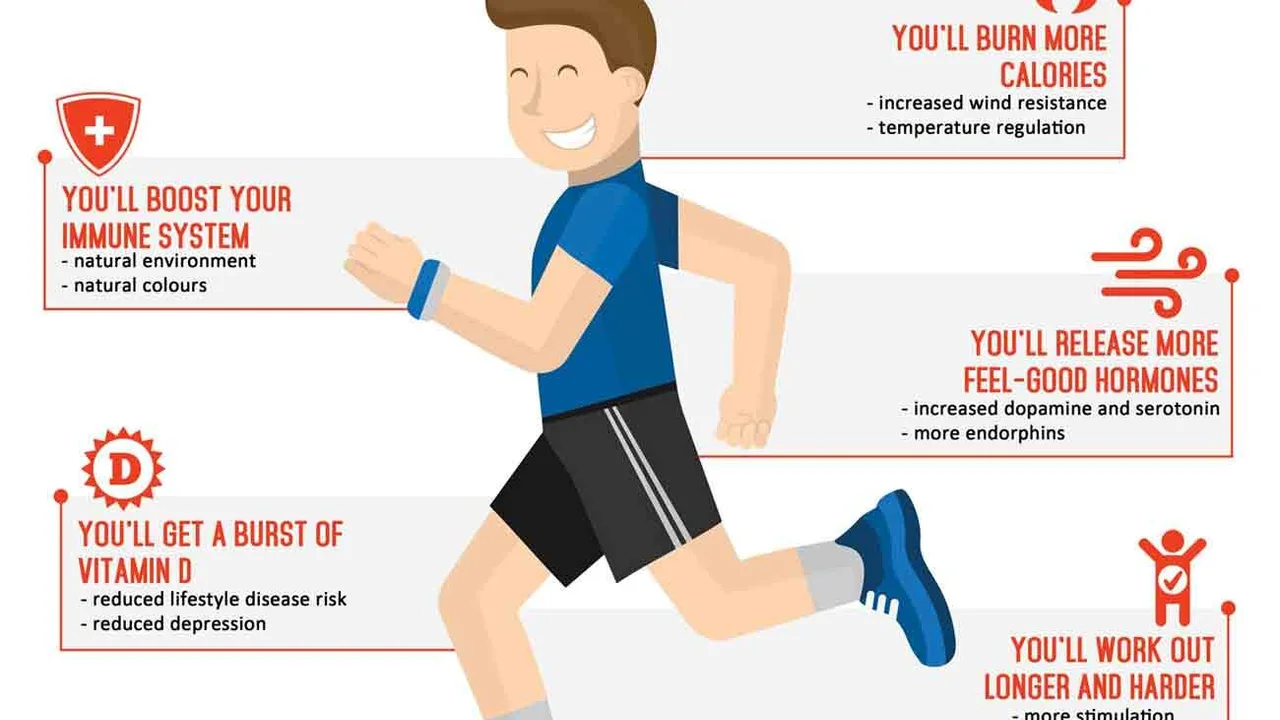
Physical Inactivity: Incorporating Exercise into Your Routine for a Stronger Heart
Lack of physical activity is a major risk factor for heart disease. Regular exercise helps strengthen your heart, lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and control weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Find activities you enjoy, and make them a regular part of your routine. Even small bursts of activity throughout the day can add up.
Unhealthy Diet: Nourishing Your Heart with a Heart-Healthy Eating Plan
What you eat has a direct impact on your heart health. A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars can increase your risk of heart disease. Focus on eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and red meat. A Mediterranean diet is often recommended for heart health.
Stress: Managing Stress Levels for Reduced Cardiovascular Strain
Chronic stress can negatively impact your heart health. It can raise blood pressure, increase inflammation, and contribute to unhealthy behaviors like overeating and smoking. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.
Family History: Understanding Your Genetic Predisposition to Heart Disease
If you have a family history of heart disease, you may be at increased risk. While you can't change your genes, you can take steps to reduce your risk by controlling other risk factors. Talk to your doctor about your family history and what you can do to protect your heart.
Lifestyle Changes for a Heart-Healthy Life: Practical Steps for Cardiovascular Prevention
Now for the good stuff! Here are some specific lifestyle changes you can make to reduce your risk of heart disease and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet: Sample Meal Plans and Recipe Ideas for Cardiovascular Health
This doesn't mean depriving yourself! It means making smart choices. Load up on fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Choose lean protein sources like fish, poultry, and beans. Use healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, and nuts. Cook at home more often so you can control the ingredients. Here are some meal plan ideas:
* **Breakfast:** Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or a whole-wheat toast with avocado and a poached egg. * **Lunch:** Salad with grilled chicken or fish, or a lentil soup with whole-grain bread. * **Dinner:** Baked salmon with roasted vegetables, or a chicken stir-fry with brown rice.Check out online resources for heart-healthy recipes. There are tons of delicious and easy options available!
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise Recommendations and Tips for Staying Motivated
As we mentioned before, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. Moderate-intensity activities include brisk walking, cycling, and swimming. Vigorous-intensity activities include running, hiking, and aerobics. Find something you enjoy and stick with it. Set realistic goals, and reward yourself when you reach them. Consider joining a gym or exercise class for added motivation. Don't forget to consult your doctor before starting any new exercise program.
Quitting Smoking: Resources and Support for Tobacco Cessation
Quitting smoking is tough, but it's the most important thing you can do for your heart health. Talk to your doctor about nicotine replacement therapy, medications, and other resources that can help you quit. Join a support group or online forum for added support. Remember, it's never too late to quit smoking.
Managing Stress: Relaxation Techniques and Mindfulness Practices for Cardiovascular Calm
Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your heart. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as:
* **Meditation:** Even a few minutes of daily meditation can help reduce stress and improve your overall well-being. * **Yoga:** Yoga combines physical activity with relaxation and mindfulness. * **Deep breathing exercises:** These exercises can help calm your nervous system and lower blood pressure. * **Spending time in nature:** Studies have shown that spending time in nature can reduce stress and improve mood. * **Connecting with loved ones:** Social support is essential for managing stress.Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Strategies for Weight Loss and Weight Management
Losing weight can be challenging, but it's worth it for your heart health. Focus on making small, sustainable changes to your diet and lifestyle. Set realistic goals, and don't get discouraged if you have setbacks. Consider working with a registered dietitian or personal trainer for guidance and support.
Medical Interventions and Treatments for Heart Disease: When and How to Seek Professional Help
Sometimes, lifestyle changes alone aren't enough to manage heart disease. In these cases, medical interventions and treatments may be necessary. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment options for your specific condition.
Medications for High Blood Pressure, High Cholesterol, and Diabetes: Understanding Cardiovascular Drug Therapies
There are many different types of medications available to treat high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes. These medications can help lower your risk of heart disease by controlling these key risk factors. Your doctor will determine the best medication for you based on your individual needs.
Angioplasty and Stenting: Restoring Blood Flow to the Heart
Angioplasty is a procedure used to open blocked arteries. A small balloon is inserted into the artery and inflated to widen the passageway. A stent, a small mesh tube, is often placed in the artery to help keep it open. Angioplasty and stenting can relieve chest pain and improve blood flow to the heart.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): Surgical Treatment for Severe Heart Disease
CABG is a surgical procedure used to bypass blocked arteries. A healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of your body and used to create a new pathway for blood to flow around the blocked artery. CABG is typically recommended for people with severe heart disease.
Specific Products and Their Uses for Heart Health: Recommendations and Comparisons
Okay, let's get into some specific products that can support your heart-healthy lifestyle. Remember to always consult with your doctor before starting any new supplements or making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Heart-Healthy Foods and Supplements: Recommendations and Comparisons
* **Omega-3 Fatty Acids:** These healthy fats are found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts. They can help lower triglycerides, reduce inflammation, and improve heart health. * **Product Example:** Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega ($30-40). This is a high-quality fish oil supplement with a good reputation for purity and potency. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Nordic Naturals to other brands like Kirkland Signature (cheaper, but may have a fishier taste) and Garden of Life (vegetarian source). Consider factors like dosage, purity, and personal preferences. * **Use Case:** Take 1-2 softgels daily with meals. * **Fiber Supplements:** Fiber helps lower cholesterol and regulate blood sugar levels. * **Product Example:** Metamucil ($15-20). A classic psyllium fiber supplement. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Metamucil to Benefiber (wheat dextrin, less likely to cause bloating) and Konsyl (another psyllium option). * **Use Case:** Mix 1-2 teaspoons with water or juice and drink immediately. * **Plant Sterols/Stanols:** These compounds can help lower LDL cholesterol. * **Product Example:** Benecol Spread ($5-7). A margarine spread fortified with plant sterols. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Benecol to Take Control (another spread) and supplements like CholestOff. * **Use Case:** Use in place of regular margarine. * **Potassium-Rich Foods:** Potassium helps regulate blood pressure. Bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, and beans are good sources. * **Product Recommendation:** Focus on getting potassium from whole foods rather than supplements. * **Use Case:** Incorporate these foods into your daily diet. * **Low-Sodium Seasonings:** Reducing sodium intake is crucial for managing blood pressure. * **Product Example:** Mrs. Dash Seasoning Blends ($3-5). A variety of salt-free seasoning blends. * **Product Comparison:** Experiment with different brands and flavors to find your favorites. * **Use Case:** Use in place of salt when cooking and seasoning food.Fitness Trackers and Smartwatches: Monitoring Physical Activity and Heart Rate
Fitness trackers and smartwatches can help you track your activity levels, heart rate, and sleep patterns. This information can be valuable for monitoring your progress and staying motivated.
* **Product Example:** Fitbit Charge 5 ($150-180). A popular fitness tracker with a good balance of features and price. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Fitbit Charge 5 to Apple Watch SE (more features, higher price), Garmin Vivosmart 4 (smaller, more discreet), and Xiaomi Mi Band 7 (budget-friendly). Consider factors like battery life, features, and compatibility with your smartphone. * **Use Case:** Wear the tracker throughout the day to track steps, heart rate, and sleep. * **Product Example:** Apple Watch Series 8 ($400-500). A smartwatch with advanced health features, including ECG and blood oxygen monitoring. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Apple Watch Series 8 to Samsung Galaxy Watch 5 (Android compatibility), Fitbit Sense 2 (focus on stress management), and Garmin Forerunner 955 (for serious athletes). * **Use Case:** Monitor heart rate, ECG, blood oxygen, and activity levels. Also provides smartphone notifications.Blood Pressure Monitors: At-Home Monitoring for Cardiovascular Health
Monitoring your blood pressure at home can help you detect high blood pressure early and track the effectiveness of your treatment. Choose a blood pressure monitor that is validated for accuracy.
* **Product Example:** Omron Platinum Blood Pressure Monitor ($80-100). A highly rated blood pressure monitor with a large display and easy-to-use interface. * **Product Comparison:** Compare Omron Platinum to other brands like A&D Medical and LifeSource. Consider factors like cuff size, accuracy, and features. * **Use Case:** Measure your blood pressure at the same time each day and record the readings.Staying Informed and Proactive: Resources for Cardiovascular Education and Support
Knowledge is power when it comes to heart health. Stay informed about the latest research and recommendations by consulting with your doctor and exploring reputable resources.
* **American Heart Association (AHA):** A leading source of information on heart disease prevention and treatment. * **National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI):** A government agency that conducts research on heart disease. * **Your Doctor:** The best source of personalized advice and guidance on managing your heart health.Remember, small changes can make a big difference. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and working closely with your doctor, you can significantly reduce your risk of heart disease and live a longer, healthier life. It's all about being proactive and taking care of yourself!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)